Binary multiplier
A binary multiplier is an electronic circuit used in digital electronics, such as a computer, to multiply two binary numbers. It is built using binary adders.
A variety of computer arithmetic techniques can be used to implement a digital multiplier. Most techniques involve computing a set of partial products, and then summing the partial products together. This process is similar to the method taught to primary schoolchildren for conducting long multiplication on base-10 integers, but has been modified here for application to a base-2 (binary) numeral system.
Contents |
History
Until the late 1970s, most minicomputers did not have a multiply instruction, and so programmers used a "multiply routine"[1][2] which repeatedly shifts and accumulates partial results, often written using loop unwinding. Mainframe computers had multiply instructions, but they did the same sorts of shifts and adds as a "multiply routine".
Early microprocessors also had no multiply instruction. The Motorola 6809, introduced in 1978, was one of the earliest microprocessors with a dedicated hardware multiply instruction. It did the same sorts of shifts and adds as a "multiply routine", but implemented in the microcode of the MUL instruction.
As more transistors per chip became available due to larger-scale integration, it became possible to put enough adders on a single chip to sum all the partial products at once, rather than reuse a single adder to handle each partial product one at a time.
Because some common digital signal processing algorithms spend most of their time multiplying, digital signal processor designers sacrifice a lot of chip area in order to make the multiply as fast as possible; a single-cycle multiply–accumulate unit often used up most of the chip area of early DSPs.
Multiplication basics
The method taught in school for multiplying decimal numbers is based on calculating partial products, shifting them to the left and then adding them together. The most difficult part is to obtain the partial products, as that involves multiplying a long number by one digit (from 0 to 9):
123
x 456
=====
738 (this is 123 x 6)
615 (this is 123 x 5, shifted one position to the left)
+ 492 (this is 123 x 4, shifted two positions to the left)
=====
56088
A binary computer does exactly the same, but with binary numbers. In binary encoding each long number is multiplied by one digit (either 0 or 1), and that is much easier than in decimal, as the product by 0 or 1 is just 0 or the same number. Therefore, the multiplication of two binary numbers comes down to calculating partial products (which are 0 or the first number), shifting them left, and then adding them together (a binary addition, of course):
1011 (this is 11 in binary)
x 1110 (this is 14 in binary)
======
0000 (this is 1011 x 0)
1011 (this is 1011 x 1, shifted one position to the left)
1011 (this is 1011 x 1, shifted two positions to the left)
+ 1011 (this is 1011 x 1, shifted three positions to the left)
=========
10011010 (this is 154 in binary)
This is much simpler than in the decimal system, as there is no table of multiplication to remember: just shifts and adds.
This method is mathematically correct, but it has two serious engineering problems. The first is that it involves 32 intermediate additions in a 32-bit computer, or 64 intermediate additions in a 64-bit computer. These additions take a lot of time. The engineering implementation of binary multiplication consists, really, of taking a very simple mathematical process and complicating it a lot, in order to do fewer additions; a modern processor can multiply two 64-bit numbers with 16 additions (rather than 64), and can do several steps in parallel—but at a cost of making the process almost unreadable.
The second problem is that the basic school method handles the sign with a separate rule ("+ with + yields +", "+ with - yields -", etc.). Modern computers embed the sign of the number in the number itself, usually in the two's complement representation. That forces the multiplication process to be adapted to handle two's complement numbers, and that complicates the process a bit more. Similarly, processors that use ones' complement, sign-and-magnitude, IEEE-754 or other binary representations require specific adjustments to the multiplication process.
Engineering approach: an unsigned example
For example, suppose we want to multiply two unsigned eight bit integers together: a[7:0] and b[7:0]. We can produce eight partial products by performing eight one-bit multiplications, one for each bit in multiplicand a:
p0[7:0] = a[0] × b[7:0] = {8{a[0]}} & b[7:0]
p1[7:0] = a[1] × b[7:0] = {8{a[1]}} & b[7:0]
p2[7:0] = a[2] × b[7:0] = {8{a[2]}} & b[7:0]
p3[7:0] = a[3] × b[7:0] = {8{a[3]}} & b[7:0]
p4[7:0] = a[4] × b[7:0] = {8{a[4]}} & b[7:0]
p5[7:0] = a[5] × b[7:0] = {8{a[5]}} & b[7:0]
p6[7:0] = a[6] × b[7:0] = {8{a[6]}} & b[7:0]
p7[7:0] = a[7] × b[7:0] = {8{a[7]}} & b[7:0]
where {8{a[0]}} means repeating a[0] (the 0th bit of a) 8 times (Verilog notation).
To produce our product, we then need to add up all eight of our partial products, as shown here:
p0[7] p0[6] p0[5] p0[4] p0[3] p0[2] p0[1] p0[0]
+ p1[7] p1[6] p1[5] p1[4] p1[3] p1[2] p1[1] p1[0] 0
+ p2[7] p2[6] p2[5] p2[4] p2[3] p2[2] p2[1] p2[0] 0 0
+ p3[7] p3[6] p3[5] p3[4] p3[3] p3[2] p3[1] p3[0] 0 0 0
+ p4[7] p4[6] p4[5] p4[4] p4[3] p4[2] p4[1] p4[0] 0 0 0 0
+ p5[7] p5[6] p5[5] p5[4] p5[3] p5[2] p5[1] p5[0] 0 0 0 0 0
+ p6[7] p6[6] p6[5] p6[4] p6[3] p6[2] p6[1] p6[0] 0 0 0 0 0 0
+ p7[7] p7[6] p7[5] p7[4] p7[3] p7[2] p7[1] p7[0] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
P[15] P[14] P[13] P[12] P[11] P[10] P[9] P[8] P[7] P[6] P[5] P[4] P[3] P[2] P[1] P[0]
In other words, P[15:0] is produced by summing p0, p1 << 1, p2 << 2, and so forth, to produce our final unsigned 16-bit product.
Engineering approach: signed integers
If b had been a signed integer instead of an unsigned integer, then the partial products would need to have been sign-extended up to the width of the product before summing. If a had been a signed integer, then partial product p7 would need to be subtracted from the final sum, rather than added to it.
The above array multiplier can be modified to support two's complement notation signed numbers by inverting several of the product terms and inserting a one to the left of the first partial product term:
1 -p0[7] p0[6] p0[5] p0[4] p0[3] p0[2] p0[1] p0[0]
-p1[7] +p1[6] +p1[5] +p1[4] +p1[3] +p1[2] +p1[1] +p1[0] 0
-p2[7] +p2[6] +p2[5] +p2[4] +p2[3] +p2[2] +p2[1] +p2[0] 0 0
-p3[7] +p3[6] +p3[5] +p3[4] +p3[3] +p3[2] +p3[1] +p3[0] 0 0 0
-p4[7] +p4[6] +p4[5] +p4[4] +p4[3] +p4[2] +p4[1] +p4[0] 0 0 0 0
-p5[7] +p5[6] +p5[5] +p5[4] +p5[3] +p5[2] +p5[1] +p5[0] 0 0 0 0 0
-p6[7] +p6[6] +p6[5] +p6[4] +p6[3] +p6[2] +p6[1] +p6[0] 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 +p7[7] -p7[6] -p7[5] -p7[4] -p7[3] -p7[2] -p7[1] -p7[0] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
P[15] P[14] P[13] P[12] P[11] P[10] P[9] P[8] P[7] P[6] P[5] P[4] P[3] P[2] P[1] P[0]
Do not be misled by the minus sign (-) notation above. It does not mean arithmetic negation ( -(7) = -7), but instead binary complementation, more commonly denoted 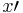 (read x prime),
(read x prime), 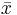 (x bar) or ~
(x bar) or ~ (tilde x), achieved by flipping all the bits. In two's complement to get the negation of a number, you complement the number then add 1, so they are NOT equivalent.
(tilde x), achieved by flipping all the bits. In two's complement to get the negation of a number, you complement the number then add 1, so they are NOT equivalent.
There are a lot of simplifications in the bit array above that are not shown and are not obvious. The sequences of one complemented bit followed by noncomplemented bits are implementing a two's complement trick to avoid sign extension. The sequence of p7 (noncomplemented bit followed by all complemented bits) is because we're subtracting this term so they were all negated to start out with (and a 1 was added in the least significant position). For both types of sequences, the last bit is flipped and an implicit -1 should be added directly below the MSB. When the +1 from the two's complement negation for p7 in bit position 0 (LSB) and all the -1's in bit columns 7 through 14 (where each of the MSBs are located) are added together, they can be simplified to the single 1 that "magically" is floating out to the left. For an explanation and proof of why flipping the MSB saves us the sign extension, see a computer arithmetic book .
Implementations
Older multiplier architectures employed a shifter and accumulator to sum each partial product, often one partial product per cycle, trading off speed for die area. Modern multiplier architectures use the Baugh–Wooley algorithm, Wallace trees, or Dadda multipliers to add the partial products together in a single cycle. The performance of the Wallace tree implementation is sometimes improved by modified Booth encoding one of the two multiplicands, which reduces the number of partial products that must be summed.
Example
See also
- Booth's multiplication algorithm
- Fused multiply–add
- Wallace tree
- BKM algorithm for complex logarithms and exponentials
- Kochanski multiplication for modular multiplication
References
- ^ "The Evolution of Forth" by Elizabeth D. Rather et. al. [1] [2]
- ^ "Interfacing a hardware multiplier to a general-purpose microprocessor"
- Computer Architecture: A quantitative Approach, Hennessy and Patterson, 1990, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc. Section A.2 (pages A-3 through A-6) and section A.9 (pages A-39 through A-49).
External links
- Multiplier Designs targeted at FPGAs
- Self-clocking Multiplier using TTL
- Binary Multiplier circuit using Half -Adders and digital gates.